How to use AI to stabilize flaky tests for good
Dmitry Reznik
Chief Product Officer

Summarize with:
German industrial study (30 developers, 1 million source lines of code) found that at least 2.5% of productive developer time is spent investigating or repairing flaky test failures. It’s not an enterprise-grade full-time; however, this volume will affect average smaller teams more significantly.
And there is still little evidence that the problem has been solved industry‑wide. In 2016, in a blog post, the Google team revealed that about 16% of their 4.2 million tests showed some level of test flakiness, which made engineers waste significant compute resources on reruns.
You may say this is a matter of maturity. And you will be right… partially. Because the root causes (asynchronous DOM hydration, race conditions in microservices, subtle environment drifts, etc.) are often invisible to standard Selenium or Playwright scripts.
And we can continue the list of issues: resource contention, shared-state dependencies, environment instability, nondeterminism — traditional one-time fixes don’t work out here.
Eventually, confidence in automation degrades, and manual testing creep returns.
This guide explains how AI test automation stabilizes flaky tests on an ongoing basis.
Why flaky tests are the perfect use case for AI
Brittle tests are often giving “data vibes”. Traditional debugging fails because it runs on a binary state — a test either passes or fails.
But in practice, the reason may be network latency spikes, DOM rendering speed, CPU contention, and third-party API response times.
It’s extremely difficult to process this multidimensional noise. We look for a broken selector, add a fixed wait, and move on. AI, in turn, analyzes execution histories across thousands of runs to identify subtle patterns that precede a failure.
- Flaky UI tests are a pattern: The solution is not just to retry a failed test. And AI correlates failures with specific environmental states: the specific test only fails when the payment API takes >200ms.
- Many signals at once: AI tools ingest logs, screenshots, network HAR files, and resource utilization metrics simultaneously and, this way, pinpoint the exact moment a test went down.
Constant reliability: Human developer fixes a test once per sprint. AI monitors stability trends 24/7, flags degrading tests, and keeps the build from breaking.
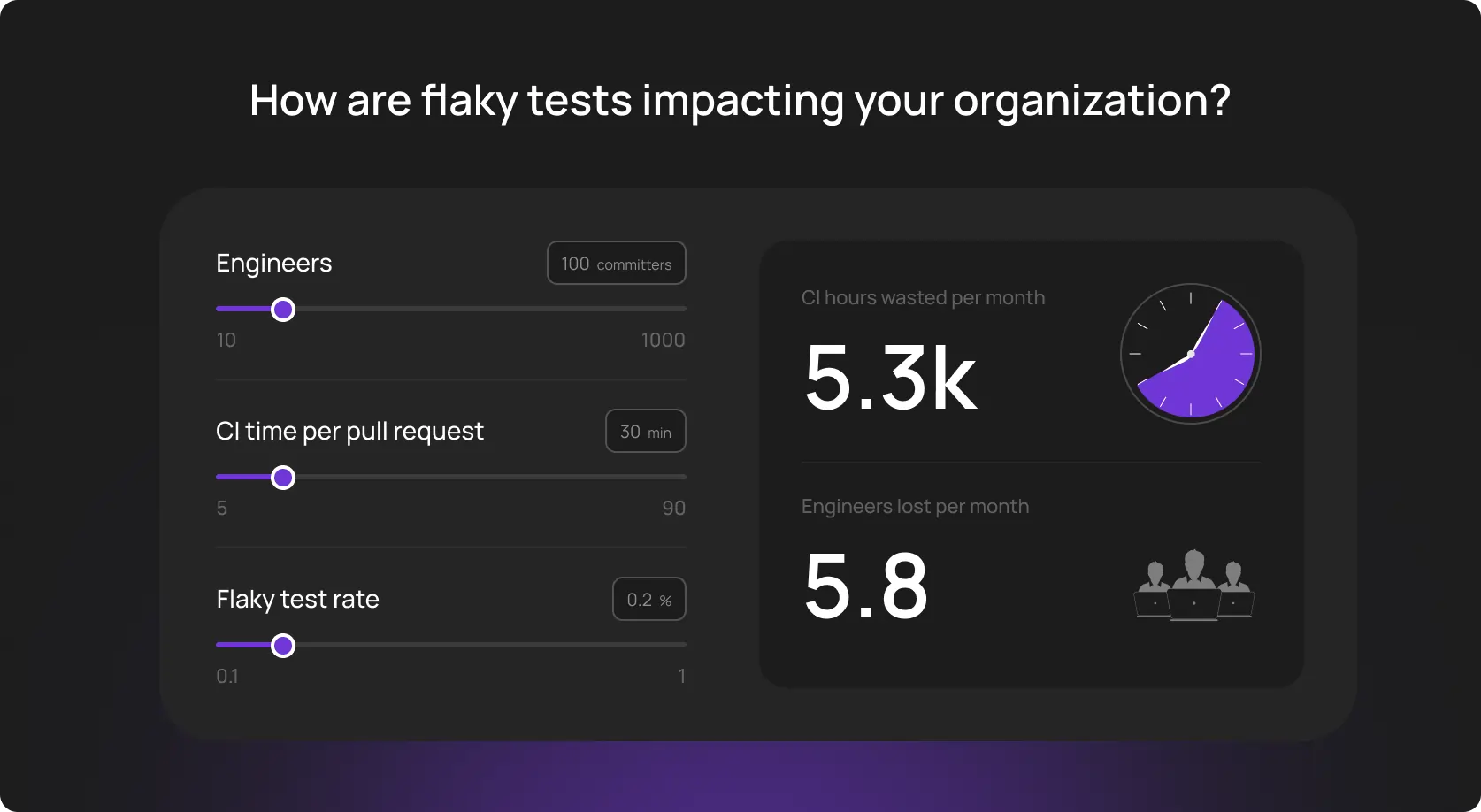
A low-hanging fruit at a glance. But not exactly. The trick hides behind the team’s ability to use artificial intelligence properly.
The real reasons flaky tests happen and why teams struggle to fix them
Flakiness is not solely a bad code, and it’s not your “underskilled” team. Look deeper — it’s a combination: code, environment, infrastructure, the team’s tech-savviness, and their problem-solving skills.
1. Unstable locators and UI changes
- Dynamic DOM, auto-generated IDs, animation-driven UI components, A/B tests, or hidden/modal elements. Tests relying on brittle XPaths or CSS selectors easily break with a UI change, even the smallest one.
- You can hardcode new locators or add more explicit wait, and this works… temporarily. You don’t want to fix the same problem every single time, do you?
2. Async/timing problems
- One of the most common causes of UI bugs is asynchronous-wait issues.
- In many environments, network latency, dynamic content loading, animations, or background API calls generate unpredictable delays. Therefore, you can’t rely on a “stable” fix, you need a “dynamic” fix that implies flexibility.
- Developers often overuse “sleep” calls or generous timeouts, which either slow down pipelines or still fail.
3. Environment drift
- A test passing locally on a MacBook M3 often fails in a constrained Linux Docker container (resource starvation).
- 46.5% of flaky tests are usually resource-affected (RAFTs). In other words, their failure is triggered solely by CPU or memory limits in the CI environment.
4. Poorly isolated test logic
- Tests with long flows often break because earlier steps leave the system in unstable or unexpected states. This is especially common when tests share databases, user sessions, or external dependencies.
- A failing test is rarely a one-time roadblock. Environmental issue weighs way more.
5. Missing or unstable test data
- As we mentioned above, shared data or third-party live data make it difficult to eliminate flaky tests. Imagine: Another tester modifies an account or a third-party API changes, and in 99% of the cases, the test will fail.
- Under these conditions, false positives make their “contribution”: the app is healthy, but the data pipeline is broken.
5 types of flaky test issues AI can diagnose and stabilize
It often looks chaotic from the outside, but there are distinct patterns. Therefore, this job is perfect for AI. OwlityAI, for example, reads multiple signals across runs, compares them, and predicts the source of the problem.
1. Locator and element instability
Changing IDs, reordered nodes, and hidden elements are some of the most recognizable sources. Artificial intelligence doesn’t have eyes, does it?
Not exactly. It uses computer vision and semantic analysis to “see” the changed element and “heal” it.
2. Timing-based flakiness
You can’t always set up a specific time slot for the button to “be interactive”. Using fixed waits often doesn't work well because conditions change across load and network stability.
AI learns how long actions take in various situations and adjusts wait times as needed.
3. Environment and infrastructure issues
CPU spikes, cold starts, and parallel runs don’t contribute to test reliability. AI “connects these dots” across environments and pipelines, spots the chain link where instability occurs, and when it’s environment-specific.
4. Test logic
We don’t want to suggest something like “only do a good job, and don’t do a poor job”. Yet, sometimes tests are flaky because they were designed in a slapdash manner. Autonomous test healing cuts redundant actions, detects unstable chains, and flags flows likely to collapse in the future.
5. Regression instability
Significant app changes frequently shake even previously reliable suites. Modern autonomous testing tools continuously scan these changes and adapt steps to keep the suite aligned with the real product.
Stabilize flaky tests with AI: 6-step workflow for teams
Important note: This workflow doesn’t replace the team, it amplifies it. An autonomous testing tool just takes over a recurrent routine (where mistakes are the most likely to happen): cross-run comparisons, repetitive triage, locator updates, low-signal debugging, etc.
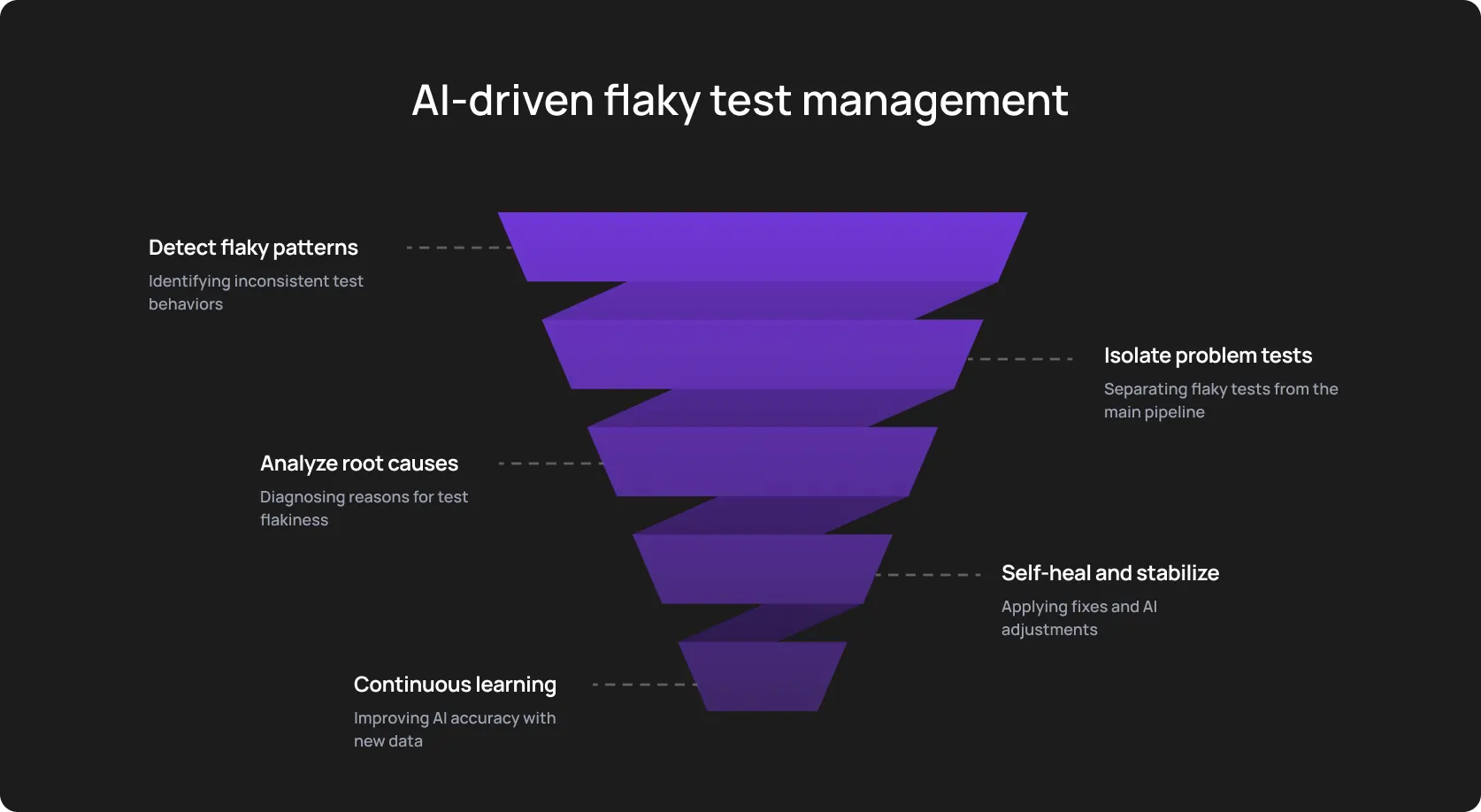
Step 1: Make an AI tool to score test stability
Start measuring and assessing test performance. Ditch the binary, pass-fail approach and start grading them.
An autonomous software testing tool assigns a “stability score” to every test case based on historical reliability. OwlityAI, for example, prioritizes tests and categorizes them (High, Medium, Low) based on risk and past performance.
Step 2: Run AI-driven root-cause classification
Another side of categorization is a specific class or type of signal. The tool looks across logs, screenshots, DOM snapshots, and timing metadata to classify the failure:
- Locator drift
- Timing race
- Environment spike
- 500 API failure
Pro tip: Watch for tests that show different failure identifiers across multiple runs. This often means that the issue combines two parameters (for example, timing and environment).
Also, pay special attention to network errors masking as UI failures. For example, when the test fails to click a button because a background API call returned a 503 error, and not because the button is missing.
AI is way better at spotting those overlaps.
Step 3: Apply autonomous test healing
After spotting the root, enable your AI end-to-end test automation tool to manage the flow without your participation.
It makes sense to control the way your tool is learning, though. It’ll self-correct using alternatives and re-run the test suite.
An ideal scenario is when the build passes, the script updates itself, and you have a coffee instead of hot-fixing a CSS selector.
Step 4: Regenerate steps using semantic understanding
When UI changes invalidate steps, AI rewrites interactions automatically using semantic knowledge of the flow. It keeps names, logic, and user intent consistent so the suite evolves alongside the product.
Step 5: Validate stability through CI pipelines
Once again on control. Integrate OwlityAI directly into your CI/CD pipeline. And then, check a bug export and a cross-section of the latest runs. This will give you a more complete picture: how many tests were “healed”, how many actually failed due to genuine bugs, and how many hours your QAs logged as their typical work.
The last one was a joke (we hope so).
To be more serious, you’ll get a batch of proof for management meetings:
- Code Stability Index (automation ROI)
- The comparison of failure patterns, performance metrics, and variance across machines.
The bottom line is the answer — does an AI tool actually improve your testing process?
Step 6: Maintain stability automatically
Another delightful feature of modern testing tools is ongoing audits. They show rising flakiness trends, the number of updated selectors and timings with every release cycle.
In addition to refactoring, test maintenance automation becomes a background service.
Successful test stability: Processes you could do with
The cost-free secret: You should treat Artificial Intelligence as a multiplicator. Is your testing chaotic? Well, AI will accelerate this chaos. If you just need an enhancement, modern tools will come in handy.
Another cost-free secret: Structure your data. These “seeds” make the difference when launching AI-powered testing. Below are two types of processes you need to make your autonomous testing efficient and effective.
Mandatory processes
1. Clear failure logging: Ditch “test failed” resolution. Detail stack traces, screenshots, network logs (HAR files), environment metadata, and context of retrying.
2. Consistent CI/CD runs: AI learns from history. Don’t change CI configurations too often. This doesn’t allow the AI model to understand what the “normal behavior” is.
3. Versioned test environments: You need stable staging environments. Don’t mash up dependencies; otherwise, AI won’t distinguish reliable data from unreliable.
4. Flakiness thresholds must be explicit: Use clear rules, like “if a test flakes >5% of the time, it is quarantined”. This gives the testing tool a clear prioritization target.
High-value processes
1. Test reliability dashboards: Visualize the trends.
2. Weekly reports: New achievements, key numbers, improvements, or insights.
3. Environment consistency policy: Strict control over container versions and data seeds.
How do you know it works: Metrics for flakiness reduction
Classical pass rate doesn’t work out as a beacon metric with AI. Even a 100% pass rate can hide an actual failure, especially if you’ve hit it after five retries. So what are the alternatives?
- Flakiness percentage drop: The frontline one — distinct flaky failures against total executions. Near-zero is possible, but it requires discipline and courage for experiments.
- Reduction in test maintenance hours: Did your team spend more time building rather than fixing? OwlityAI, for example, usually shows a 70-80% drop in this metric.
- Time saved per PR/CI run: How much faster do developers get feedback? Logic here is simple: fewer retries, no scaling threads in the cloud → feedback loop gets faster.
- Mean time to diagnose (MTTD) failures: The time from identifying the failure to determining the cause.
- Stability score increase: Track the “Code Stability Index”. It basically shows whether you managed to stabilize flaky tests.
- Reduction in test retries: Every retry costs money (cloud compute). Fewer retries → less puffed your bill.
When AI is the perfect solution for flaky tests
If you check 3+ boxes below = you need to use AI.
- Test suite volume > human analytical capabilities: You have thousands of tests, nobody knows which ones are actually valid anymore, and humans need like 10ish years to comprehend the entire testing system.
- CI pipelines blocked by false alarms: Developers ignore red builds because “it’s probably just the tests acting up again”.
- UI changes frequently: Your frontend is React/Angular/Vue, and your team can’t keep up with the selector churn.
- You operate on many platforms: Cross-browser and mobile matrices create variance that is hard to replicate locally.
- You have no trust: You feel a real trust gap among developers, and they don’t support the way you ensure test reliability.
When AI will not fix flaky tests
We all know that artificial intelligence is not a silver bullet for now. Especially in software testing, where you should deeply understand the business context and human irrational behavior. Check the points below. If you noticed something similar to your testing reality, AI likely doesn’t resolve the system.
- No stable environments: Database and environments differ significantly from run to run, AI won’t determine a “normal” baseline. Chances are, it will flag every run as an anomaly.
- No CI observability: Without access to network logs, console errors, and resource utilization metrics, AI is unable to distinguish between a UI bug and a 503 Service Unavailable error.
- Zero test coverage for core flows: You can’t deal with something that doesn’t exist. AI model requires an existing corpus of executions to identify patterns.
Noticeable. 95% of GenAI pilots failed to return value. There is a 17% increase from 2024 in companies that gave up AI implementation. Why? Because it’s difficult to establish a robust building on an unstable foundation.
Pro tip: If your environment uptime is below 99%, your data seeding is a spray-and-pray strategy. Implement strict version control and deterministic infrastructure first.
Risks to watch for when using AI for test stabilization
AI-powered testing comes with many risks. Below are just four general ones. Our call here is to stay alert and look for additional risks that are related to your specific case.
- Self-healing masking real bugs: A poorly tuned self-healing agent might find a Submit button that has been visually hidden by a CSS regression. The tool “heals” the locator, clicks the hidden button via JavaScript, and passes the test. Eventually, the test passes, but the user can’t actually click the button. And now imagine if this is not a submit button, but a payment one.
- AI with no real ML: This clumsy phrase means that the virtual machine doesn’t learn from your data, and thus, is too generic. There are too many retry-tools under the autonomous solutions for your testing.
- Over-reliance on retries: This is another side of the previous problem. Retrying a test 10 times until it passes, isn’t stabilizing but brute-forcing.
- Test data strategy isn’t documented: Without controlled, consistent, and isolated test data, even the most advanced AI testing tool acts against polluted signals and brings about the opposite effect.
Bottom line
We don’t want to hyperbolize, but it’s true, flakiness keeps you from faster time-to-market and better user experience. At the bottom line, it affects your business success and profit.
Of course, this is only one aspect of the complex business machine, but it’s definitely worth attention.
This is why we created OwlityAI with computer vision, self-healing tests, and many other strategic features. But we can’t help warning: If you don’t have the foundation in data strategy, robust infrastructure, and learning program for staff, you won’t get much profit from test maintenance automation and semantic AI.
Start with the base, start small, and scale after first wins. If you have some wins but don’t understand how to scale the initial success, book a demo with OwlityAI experts. We’ll be happy to help.
Monthly testing & QA content in your inbox
Get the latest product updates, news, and customer stories delivered directly to your inbox